ERA-Interim: derived components
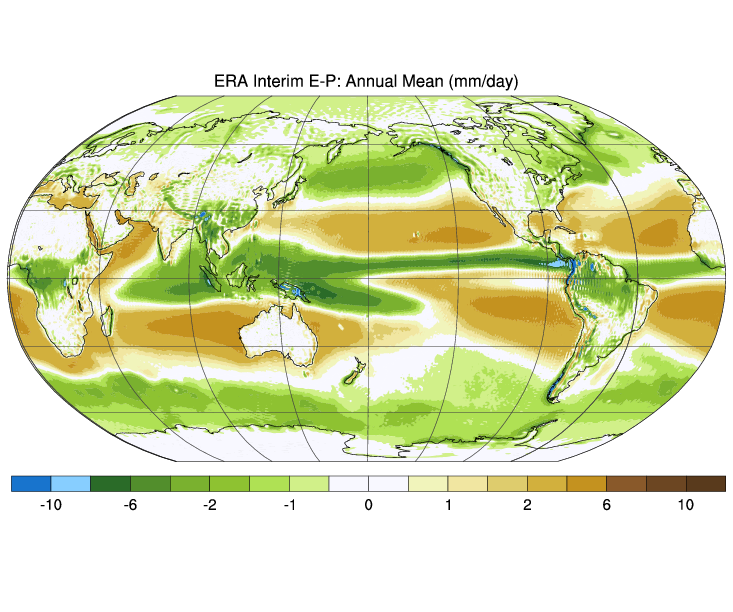
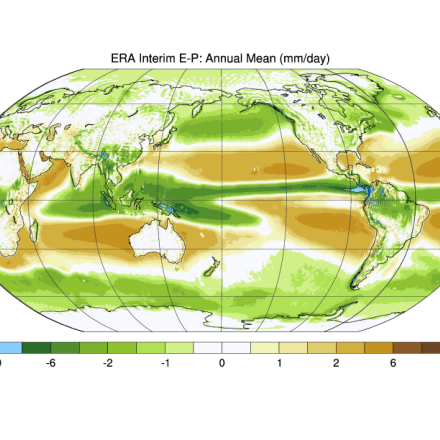
Era-Interim data are used to derive monthly mass, moisture and energy budget products. Each term is available. Atmospheric energy, mass, and moisture budgets can be computed by vertically integrating reanalysis fields and employing suitable corrections (e.g. mass). The budgets are uniquely valuable for interpreting the climate's mean state and its variability. They can also be used in conjunction with complementary data (i.e. top of atmosphere fluxes) to diagnose the surface energy budget and over large scales these estimates can rival or surpass other methods for doing so.
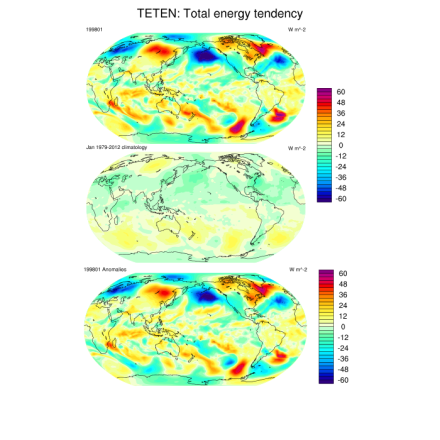
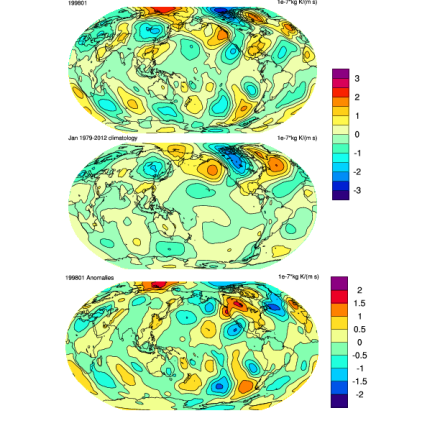
The total atmospheric energy budget consists of the combined dry static energy (Cp•T+g•Z), latent energy (Lv•Q), and kinetic energy terms, the tendency and divergence of which can be explicitly computed. These fields are available individually, or in sum as total energy divergence (TEDIV) and total energy tendency (TETEN). All budget fields are computed on monthly timescales on the native model grid.
Terms available and their definition:
TEDIV = DSEDIV + LEDIV + KEDIV
TEDIV = del•(Cp•UT+ g•UZ+L•UQ+ UK, Cp•VT+ g•VZ+L•VQ+ VK)
DSEDIV = del•(Cp•UT+ g•UZ, Cp•VT+ g•VZ)
LEDIV = del•(L•UQ, L•VQ)
KEDIV = del•(UK, VK)
Cite this page
Acknowledgement of any material taken from or knowledge gained from this page is appreciated:
National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff (Eds). Last modified "The Climate Data Guide: ERA-Interim: derived components.” Retrieved from https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/era-interim-derived-components on 2026-02-27.
Citation of datasets is separate and should be done according to the data providers' instructions. If known to us, data citation instructions are given in the Data Access section, above.
Acknowledgement of the Climate Data Guide project is also appreciated:
Schneider, D. P., C. Deser, J. Fasullo, and K. E. Trenberth, 2013: Climate Data Guide Spurs Discovery and Understanding. Eos Trans. AGU, 94, 121–122, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013eo130001
Key Figures
Other Information
- Trenberth, K. E. and J. T. Fasullo, 2011: Tracking Earth's energy: From El Niño to global warming. Surveys in Geophysics, Special Issue
- Trenberth, K. E., J. T. Fasullo, and J. Mackaro, 2011: Atmospheric moisture transports from ocean to land and global energy flows in reanalyses. J. Climate, 24, 4907-4924