CloudSat
CloudSat is a satellite mission designed to measure the vertical structure of clouds from space. The radar data produces detailed images of cloud structures.
CloudSat is one of a constellation of satellites known as the A-Train (Cloudsat, CALIPSO, PARASOL, Aqua, Aura, GCOM-W1). The satellites fly in a nearly circular orbit with an equatorial altitude of approximately 705 km. The orbit is sun-synchronous, maintaining a roughly fixed angle between the orbital plane and the mean solar meridian. CloudSat maintains a close formation with Aqua and a particularly close formation with CALIPSO, providing near-simultaneous and collocated observations with the instruments on these two platforms.
CloudSat data are available as Level-2 and as part of the Cloud Feedback Model Intercomparison Project (CFMIP) .
Key Limitations
Expert Developer Guidance
Cite this page
Acknowledgement of any material taken from or knowledge gained from this page is appreciated:
National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff (Eds). Last modified "The Climate Data Guide: CloudSat.” Retrieved from https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/cloudsat on 2026-02-27.
Citation of datasets is separate and should be done according to the data providers' instructions. If known to us, data citation instructions are given in the Data Access section, above.
Acknowledgement of the Climate Data Guide project is also appreciated:
Schneider, D. P., C. Deser, J. Fasullo, and K. E. Trenberth, 2013: Climate Data Guide Spurs Discovery and Understanding. Eos Trans. AGU, 94, 121–122, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013eo130001
Key Figures
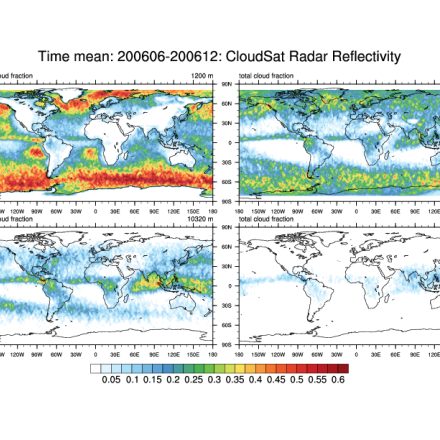
Time mean total cloud fraction at various levels for June-Dec, 2006. (Climate Data Guide; D. Shea: see: http://www.ncl.ucar.edu/Applications/cloudsat.shtml)
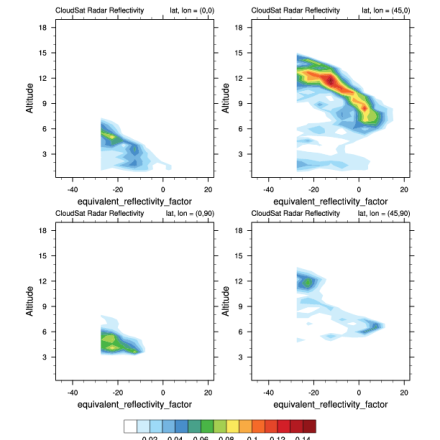
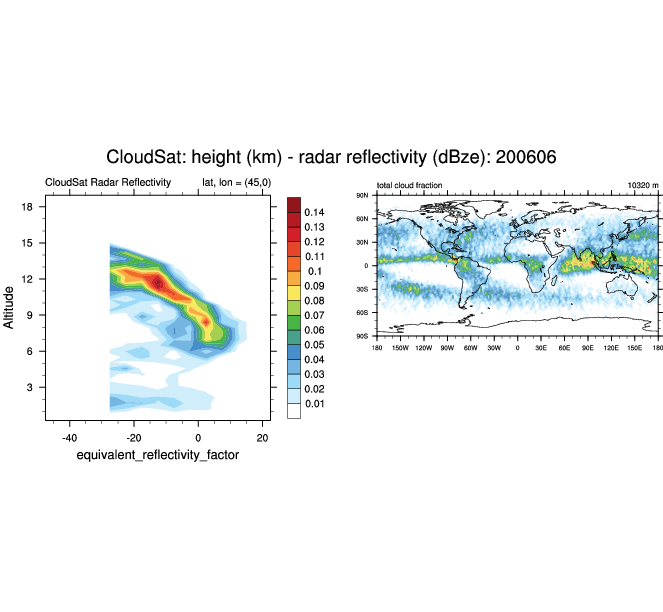
Radar reflectivity at various locations for June, 2006. (Climate Data Guide; D. Shea: see http://www.ncl.ucar.edu/Applications/cloudsat.shtml)
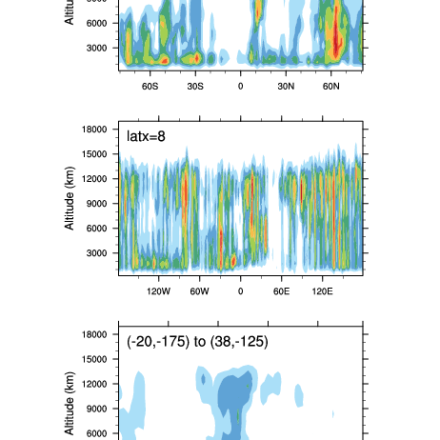
Vertical cross sections at 150W (81S-81N), 8N (179W-179E) and a cross section spanning (20S,175W) to (38N,125W). (Climate Data Guide; D. Shea: see http://www.ncl.ucar.edu/Applications/cloudsat.shtml)
Other Information
- Zhang , Y .et al (2010): Evaluation of tropical cloud and precipitation statistics of Community Atmosphere Model version 3 using CloudSat and CALIPSO data, J. Geophys. Res., 115, D12205
- Mace, G. G., et al. (2009): A description of hydrometeor layer occurrence statistics derived from the first year of merged CloudSat and CALIPSO data, J. Geophys. Res., 114, D00A26
- Marchand, R.T, et al (2009): A comparison of simulated cloud radar output from the multi-scale modeling framework global climate model with CloudSat cloud radar observations, J. Geophys. Res., 114, D00A20
- Marchand, R. T. et al (2008): Hydrometeor detection using CloudSat-an earth orbiting 94 GHz cloud radar. J. Atmos. Oceanic. Technol., 25, 519-533
- Stubenrauch, C., W. Rossow and S. Kinne (2012), Assessment of Global Cloud Data Sets from Satellites, A Project of the World Climate Research Programme Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment Radiation Panel, WCRP Report No. 23/2012, 176 pp (.pdf).