Simplistic Overview of Reanalysis Data Assimilation Methods
Cite this page
Acknowledgement of any material taken from or knowledge gained from this page is appreciated:
National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff (Eds). Last modified "The Climate Data Guide: Simplistic Overview of Reanalysis Data Assimilation Methods.” Retrieved from https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/simplistic-overview-reanalysis-data-assimilation-methods on 2026-03-03.
Citation of datasets is separate and should be done according to the data providers' instructions. If known to us, data citation instructions are given in the Data Access section, above.
Acknowledgement of the Climate Data Guide project is also appreciated:
Schneider, D. P., C. Deser, J. Fasullo, and K. E. Trenberth, 2013: Climate Data Guide Spurs Discovery and Understanding. Eos Trans. AGU, 94, 121–122, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013eo130001
Key Figures
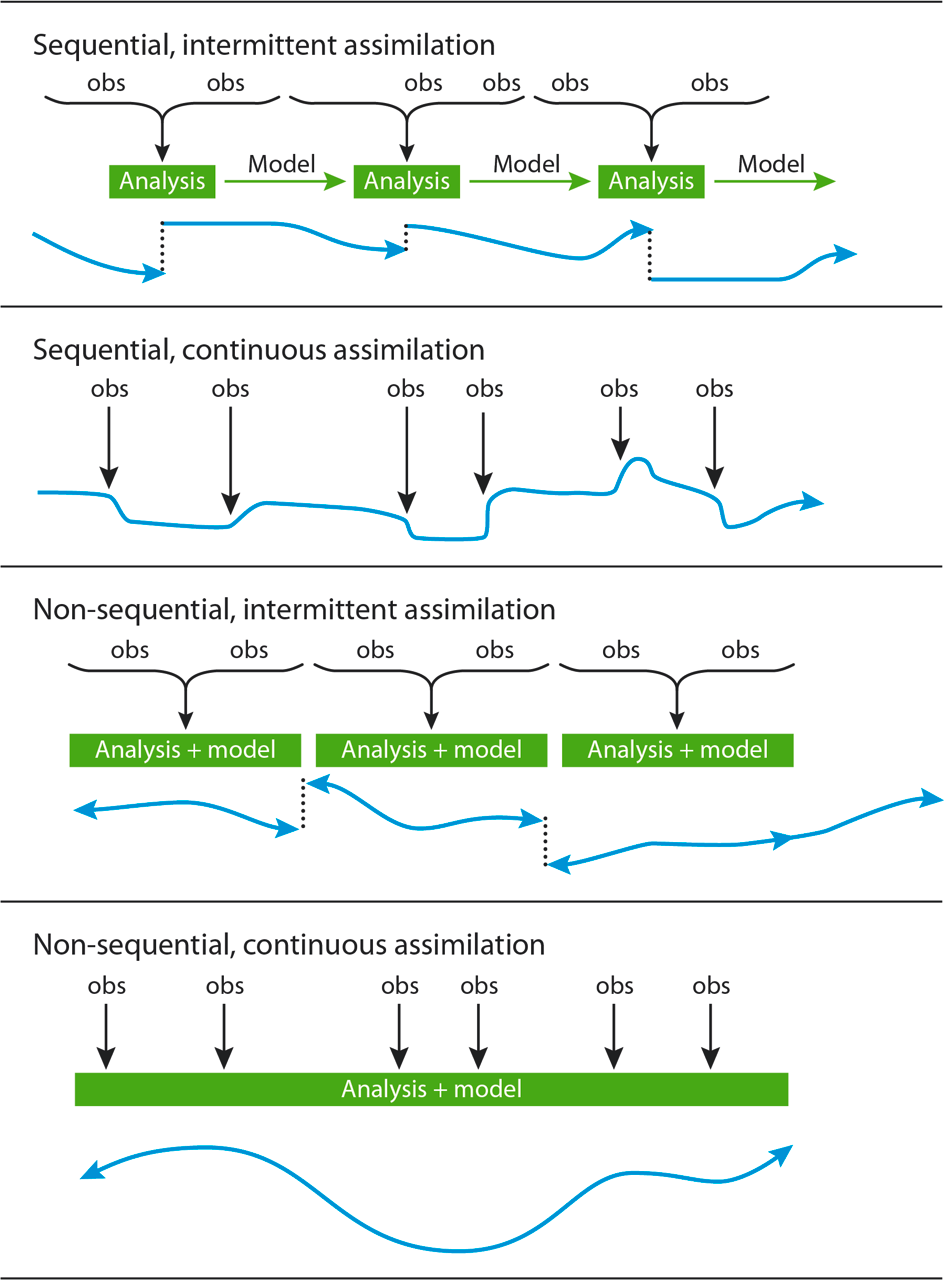
Figure 1 . Representation of four basic strategies for data assimilation, as a function of time. The way the time distribution of observations ("obs") is processed to produce a time sequence of assimilated states (the lower curve in each panel) can be sequential and/or continuous. (Source ECMWF: figure and caption)
Other Information
- Courtier, P., J.-N. Thépaut and A. Hollingsworth, 1994: A strategy for operational implementation of 4D-VAR, using an incremental approach. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 120, 1367-1387.
- Courtier, P., E. & coauthors, 1998: The ECMWF implementation of three-dimensional variational assimilation (3D-Var). Part 1: formulation. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 124, 1783-1807.
- Daley, R., 1991: Atmospheric Data Analysis. Cambridge Atmospheric and Space Science Series, Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-38215-7, 457 pages.