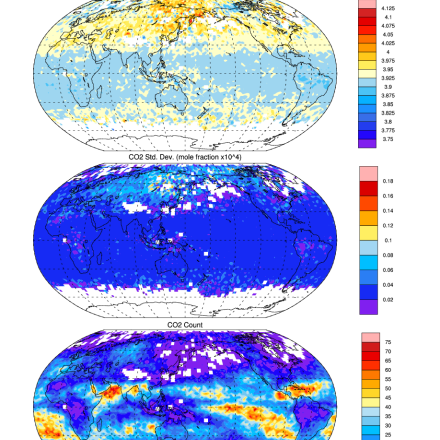
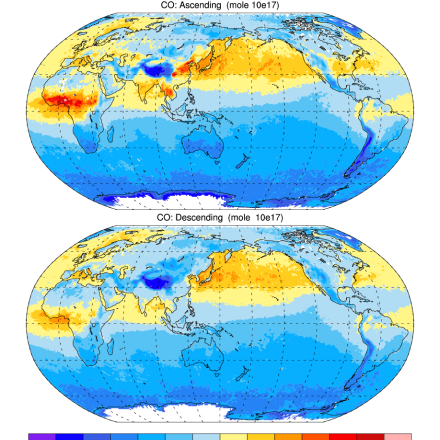
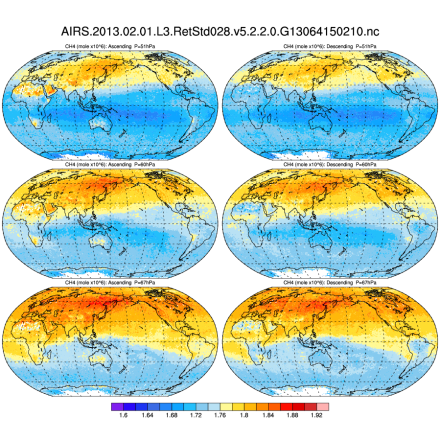
AIRS and AMSU: Trace Gases (CO2, CO, CH4, O3...); Level 3
Key Strengths
Key Limitations
Cite this page
Acknowledgement of any material taken from or knowledge gained from this page is appreciated:
National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff (Eds). Last modified "The Climate Data Guide: AIRS and AMSU: Trace Gases (CO2, CO, CH4, O3...); Level 3.” Retrieved from https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/airs-and-amsu-trace-gases-co2-co-ch4-o3-level-3 on 2026-02-23.
Citation of datasets is separate and should be done according to the data providers' instructions. If known to us, data citation instructions are given in the Data Access section, above.
Acknowledgement of the Climate Data Guide project is also appreciated:
Schneider, D. P., C. Deser, J. Fasullo, and K. E. Trenberth, 2013: Climate Data Guide Spurs Discovery and Understanding. Eos Trans. AGU, 94, 121–122, https://doi.org/10.1002/2013eo130001
Key Figures
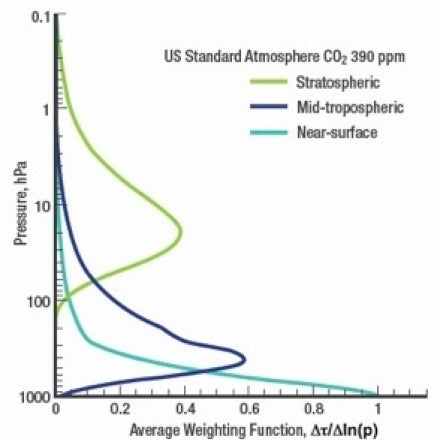
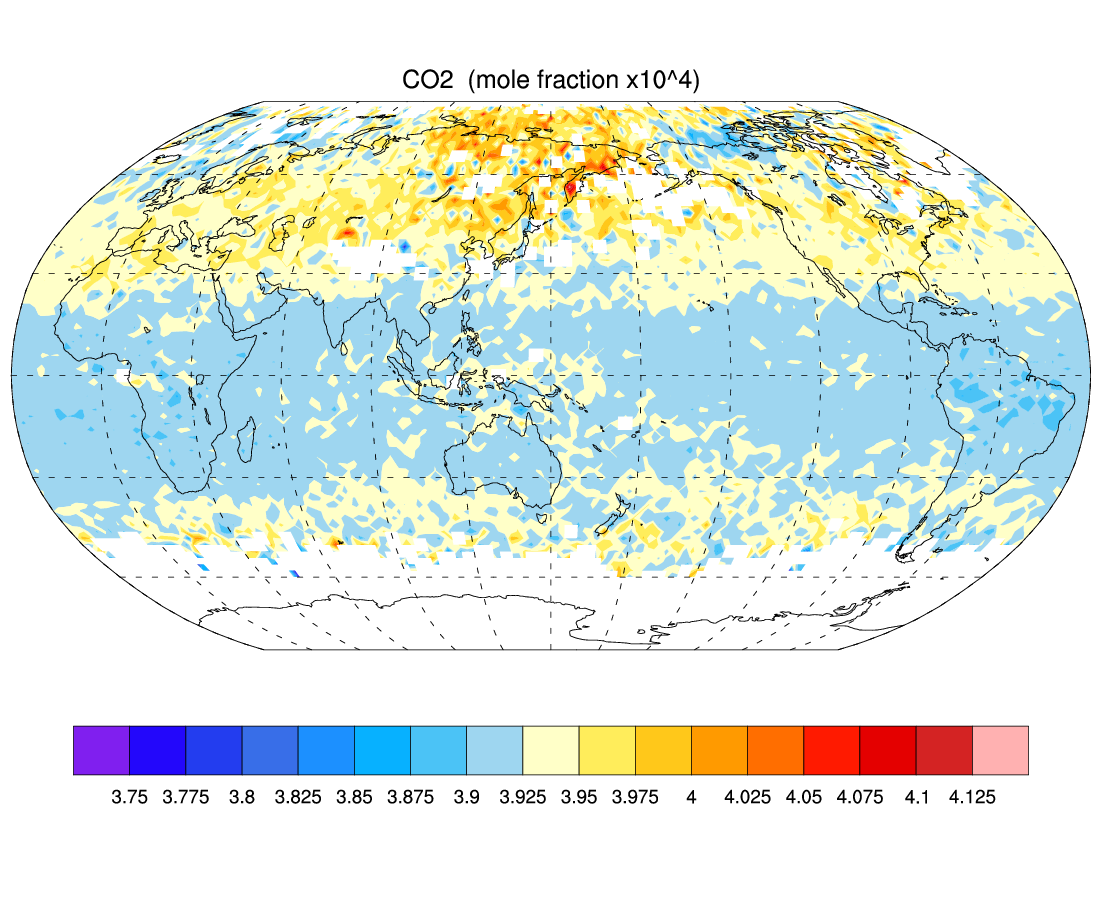
AIRS sensitivity to carbon dioxide with altitude. Source: http://airs.jpl.nasa.gov/data/about_airs_co2_data/
Other Information
- Chahine, M.T. et al. (2008): Satellite Remote Sounding of Mid-Tropospheric CO2 . Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, September
- Strow, L.L. & S.E. Hannon (2008): A 4-year Zonal Climatology of Lower Tropospheric CO2 Derived from Ocean-Only Atmospheric Infrared Sounder Observations. J. Geophys. Res., 29
- Engelen, R.J et al (2009): Four Dimensional Data Assimilation of Atmospheric CO2 Using AIRS Observations.
- Maddy, E.S. et al (2009): CO2 Retrievals from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder: Methodology and Validation
- Rajab, J. M. et al (2012), Methane Interannual Distribution over Peninsular Malaysia from Atmospheric Infrared Sounder Data: 2003-2009, Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 12(6), 1459-1466
- Zhang, Y. et al (2012): Retrieval of methane profiles from spaceborne hyperspectral infrared observations. J. of Remote Sensing, v. 16, no. 2, p. 232-247
- Xiong, X. et al (2008): Characterization and validation of methane products from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS), J. Geophys. Res., 113, G00A01